AnsTest is a module for the interpretation of aquifer test
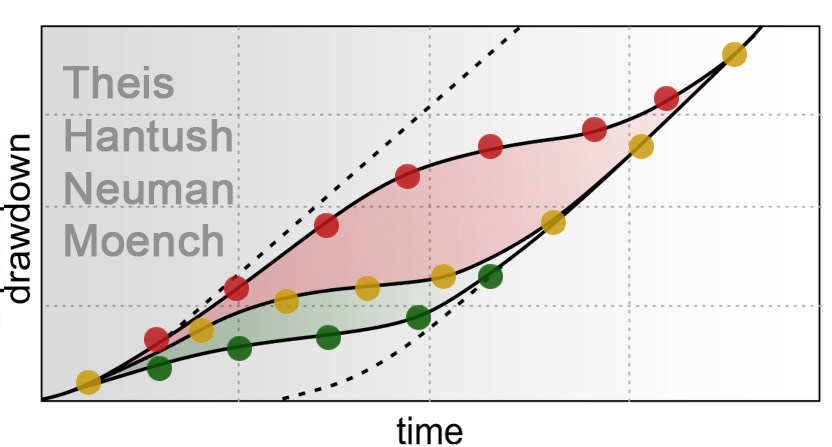
Pumping Tests
The most common aquifer test consists of pumping from a well at a controlled rate and measuring the water-level response in the same well or in surrounding observation wells. This kind of test is used to determine hydraulic properties of the tested aquifer.
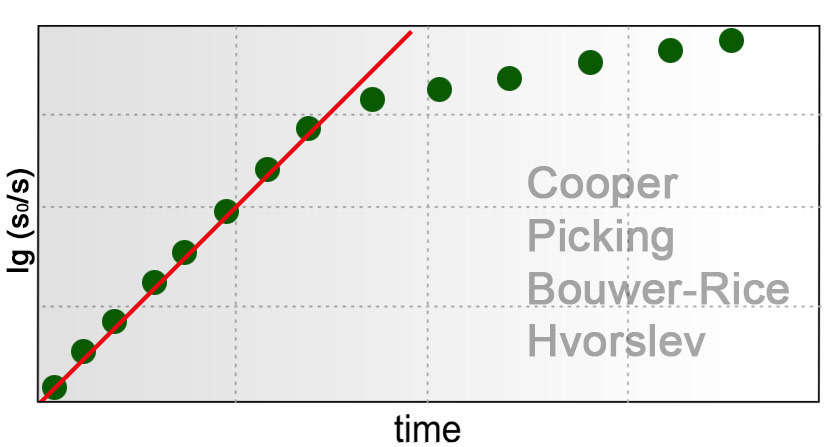
Slug Tests
A type of field experiment where a slug of water is quickly (the interpretation assumes -instantaneously) added or removed from a groundwater well, and the water level response is monitored through time.
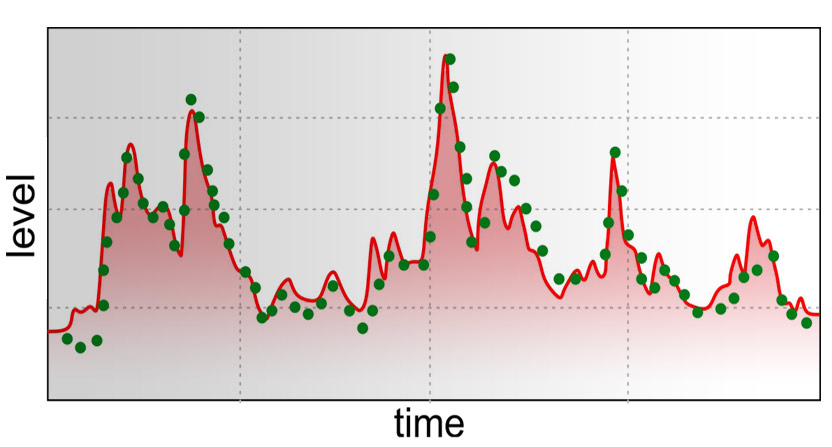
Stream-aquifer Tests
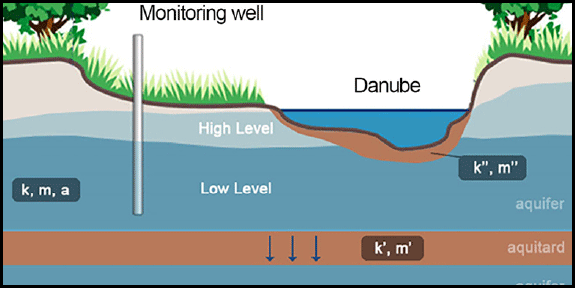
Combined analysis of well and stream hydrographs to determine the properties of a stream bed and an underlying aquifer. This method can also be used to determine isolating properties of lake bottom sediments.
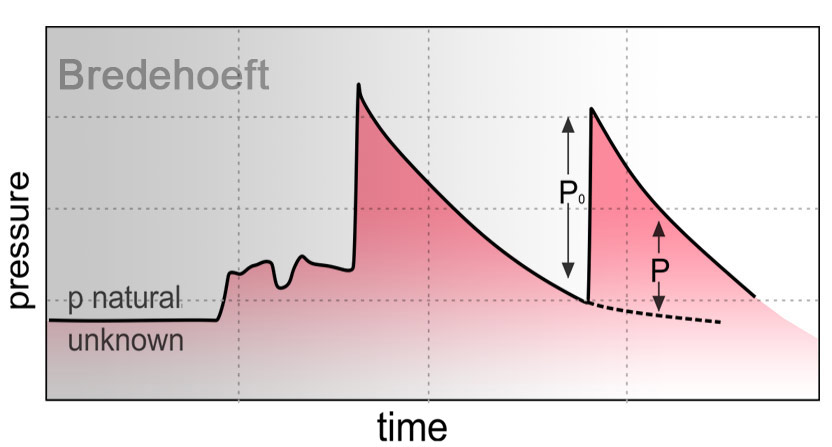
Pulse Tests
In a pulse test, an increment of pressure is applied to a well interval that is isolated by packers. Reduction of pressure is monitored within the same zone using automatic recording pressure transducers. This type of field experiments is most common in low-permeable rocks.
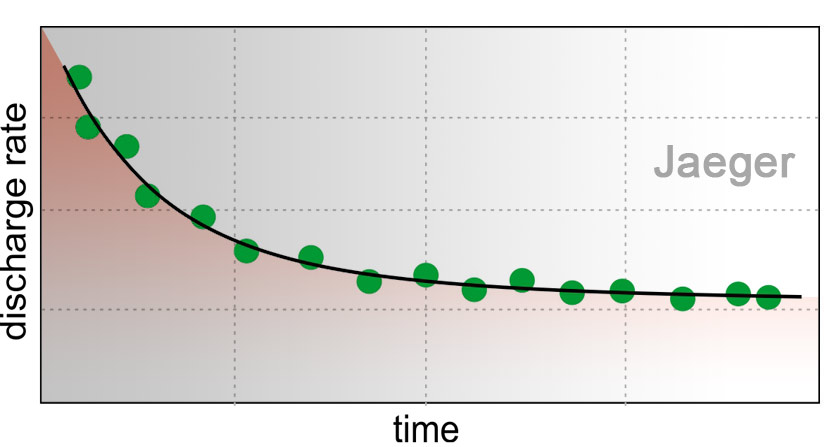
Constant-Head Tests
Aquifer test in which the piezometric head (drawdown) in a well is maintained at a constant level, while water discharge rate is monitored. A typical application is an aquifer test in a flowing artesian borehole, where the potentiometric surface is above ground level.
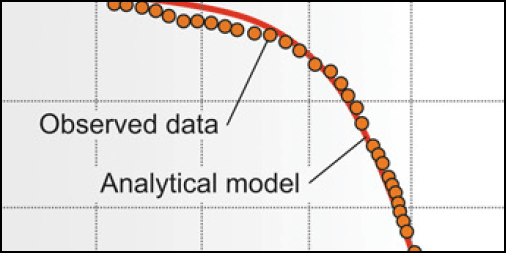
Analysis workflow: selection of analytical solution is easy with AnsTest-guided process.
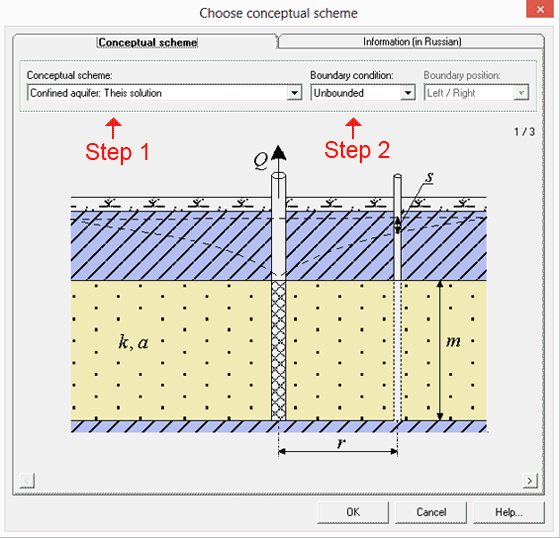
Step 1. Choose a conceptual scheme.
Step 2. Define the type of boundaries.
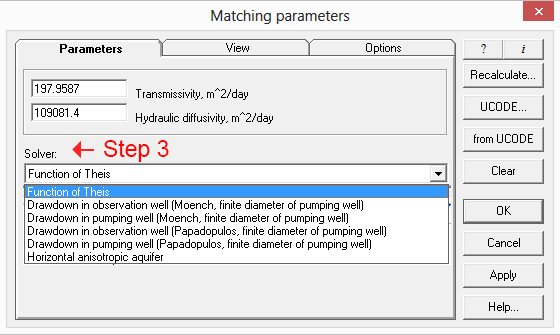
Step 3. In the “matching parameters” window select an analytical solution from the list. The solutions are already pre-selected by AnsTest considering the specific hydrogeological conditions and boundaries.
Supported type of hydrogeological conditions
Aquifers
1. Non-leaky confined aquifer
2. Point source in confined profile anisotropic aquifer
3. Linear source in confined aquifer that is anisotropic on the vertical plane
4. Unconfined aquifer
5. Leaky aquifer system
6. Two-layer aquifer system (unconfined aquitard above confined aquifer)
7. Arealy heterogeneous aquifer
8. Pumping near river
9. Multi-layer aquifer systems (two- or three-layer)
10. Fracture
Boundaries
1. Aquifer of infinite lateral extent
2. Semi-infinite aquifers
3. Strip aquifers
4. Wedge-shaped aquifers
5. Rectangular aquifers
6. Circular aquifers
Case Studies
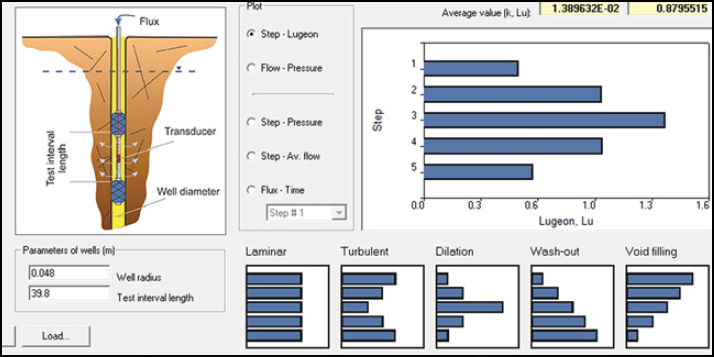
Interpretation of packer tests in fractured schists, Olimpiada open pit in the Krasnoyarsk region (Russia)
Client: Polyus Gold
Objective: Determination of hydraulic conductivity in low-permeable schist formations
Method: Lugeon test tool in Hydrogeologist Workbench
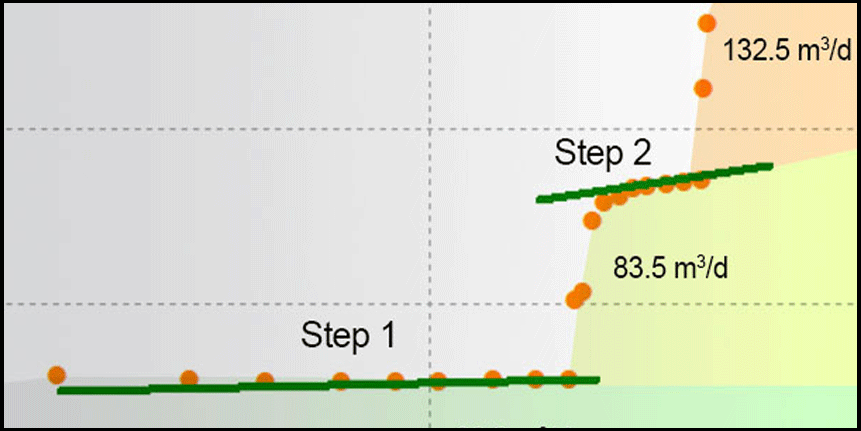
Interpretation of a step-drawdown test to plan for a constant rate pump test in St-Petersburg
Client: Municipal government of St-Petersburg, Russia
Objective: Determine well efficiency and optimal pumping rate for a constant rate pump test
Method: Interpretation of step-drawdown tests in ANSDIMAT+
Slug tests in packer-isolated intervals for planning Radioactive waste disposal (Krasnoyarsk region, Russia)
Client: Russian state company
Objective: Determination of hydraulic conductivity changes with depth in fractured gneiss rocks
Method: Interpretation of slug-tests on packer-isolated intervals